The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
The tech we use nowadays is the outcome of a number of artificial intelligence milestones achieved by many unsung heroes. We travelled back in time and compiled a list of all significant artificial intelligence achievements that have allowed us to enjoy our current lifestyle. Let’s take a look at AI evolution over time. The timeline below highlights AI milestones that have been achieved throughout history. These achievements can be found in all areas of Artificial Intelligence. Because this is a growing timeline, new milestones will be updated on a regular basis.
Timeline
Stanford Cart As An Autonomous Road Vehicle By Les Earnest
Earnest discussed the cart with Adam (the first developer of the cart) to build a robot as a road vehicle visual-based guidance. Initially, Braised, with Rodney Schmidt’s collaboration, created a T transmitter with low power and a radio-based control link to start the project. With the KA10 processor’s usage ran..Read more
Heuristic Programming Project (HPP) initiated by Ed Feigenbaum
Heuristic Programming Project (HPP) is widely used in AI applications related to Biology and Medicine. The project’s research focus was on applications-based research, AI-based research, community tools, activities, and methodologies required to build an Expert System. The programs designed using HPP could assist in problem-solving techniques, an excellent skilled vehicle..Read more
WABOT-1 Built At Waseda University in Japan
WABOT-1 was the first fun purpose robot developed in the world. It has a limb control system, a conversation system, and a vision system. WABOT could communicate with a man in the Japanese language. It has artificial eyes, ears, and a mouth that act as receptors and help him measure..Read more
SHRDLU Computer Program Developed By Terry Winograd
SHRDLU computer program is based on natural language processing, developed at MIT in 1968-1970. A person talks to a computer in a more geometric language like moving objects, naming the things, and fitting each item in “Blocks world.” The geometric words coded in the program were like pyramid, cone, blocks,..Read more
SCHOLAR Program Developed By Jaime Carbonell
SCHOLAR program developed by Jaime Carbonell at Stanford was the first Intelligent Tutoring System(ITS) in the late 1969’s. SCHOLAR development was based on Computer-Assisted Instruction(CAI), and it provided high speed & timely throughputs that have changed the progress of educational technologies and student learnings. The tutorial system of SCHOLAR enables..Read more
Augmented Transition Networks Described By Bill Woods
Augmented Transition Networks (ATN’s) are embedded in the systems based on Natural Languages and the questions answering based systems to recognize both speech and text inputs. They are flexible, easy to code & debug, behave cooperatively to handle multiple syntax-related constructions, and provide a user-friendly interface to interact with the..Read more
Stanford Arm Developed By Victor Scheinman AT SAIL
Stanford Arm was mounted on a large table with computer video cameras and some other operative tools. This device facilitated researchers and students for more than 20 years. It was also used in education because of its easy maintenance and reliability characteristics. The arm is not humanoid, and it has..Read more
Perceptrons: An Introduction To Computational Geometry
Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert highlighted limitations in the capabilities of simple neural networks. Perceptrons are the major concern of this book that is an Artificial Intelligence Neural network. This book changed the research directions of A.I. An extended version of the same research published by authors in 1988. The..Read more
Backpropagation Described By Arthur Bryson & Yu-Chi Ho
Backpropagation is an optimization method used for multi-level dynamic systems. As a learning algorithm for multi-stage Artificial Intelligence Neural Networks, it contributes to the successive progress of deep learning from the 2000s to 2010s. Now computing has achieved considerable advancement to manage effectively the training of networks operating on a..Read more
Internet with DARPA Program Invention
Internet with DARPA program is developed in 1969. The”Man-Machine Symbiosis” proposal by Licklider is the fundament for the development of the ARPANET. Licklider also used the concept of ” Cyborg Intelligence” to train the machine to work according to human requirements. As a director of the ARPANET, he worked to..Read more
A* Search Algorithm Developed At Stanford University
A* also pronounced as A-asterisk, which was designed by expert researchers in 1968. The A* search algorithm is mostly used as an algorithm to find the path by traversing the data structures like graphs. The wide use of the A* algorithm in computer games such as it is used to..Read more
The Computer Forum: An Industrial Affiliates Group
“The Computer Forum,” an industrial affiliates group, started by Professors Ed McCluskey, Arthur Samuel, and Bill Miller. After its founding, the forum has started to invite experts word wide, especially those who belonged to Silicon Valley as corporate members. Industrial and academic leaders related to Electrical Engineering and Computer Science..Read more
A Space Odyssey: HAL featured film Directed By Stanley Kubrick
Stanley Kubrick directed a HAL (Heuristically Programmed Algorithmic Computer) featured science fiction film 2001 “A Space Odyssey,” is released. HAL’s main functions are to control systems related to spacecraft and have efficient interactions with the ship’s crew and communicate like a human being until a malfunction causes to change the..Read more
The Digital Systems Laboratory Established At MIT
The Digital Systems Laboratory was established at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Later the name changed to “Computer Systems Laboratory.” The main aim behind the development was to facilitate the undergraduate students to observe & understand Digital Systems’ operations. While performing experiments, students were also encouraged with theory contents in..Read more
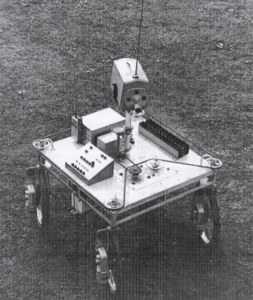
Charles Rosen Developed Shakey
Charles Rosen developed a robot named “Shakey,” which was the first general-purpose mobile robot. It efficiently perceives from its operating environment, derives implicit facts from available explicit points, makes plans, recovers successfully from errors during execution of the plan, and communicates in English. Shakey was programmed using LISP and FORTRAN,..Read more
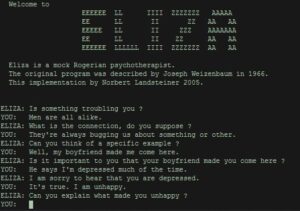
Joseph Weizenbaum Created ELIZA
ELIZA was the earliest NLP program at MIT AI laboratory. It made conversation through natural language between human and machine possible. The conversation was simulated by the program using “Pattern Recognition” and “substitution methodology”. But this was just a mimicry illusioned by machine, and no contextualization was provided to the..Read more
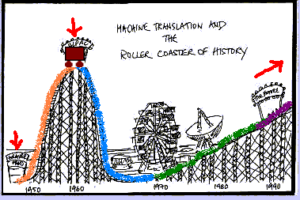
The ALPAC Report In Machine Translation History
The ALPAC report’s main goal was to observe the progress of machine translation, particularly and computational linguistics generally. The research recommendations were: effective translation evaluation, a speedy process for human translation, cost and quality of translation sources, protection against translation produced, eliminate delays in the translation process, and speed and..Read more
First Ultra Intelligent Machine Defined By IJ Good
In “Speculations Concerning the First Ultra intelligent Machine,” IJ Good” well-defined the Ultraintelligent Machine as: “this machine has the great and efficient abilities to surpass human beings in their mental and logical activities.” Since the goal behind the development of an Ultra intelligent Machine is intellectual tasks, such machines are..Read more
DENDRAL Project At Stanford University
The DENDRAL term is derived from the Dendritic Algorithm. In the 1960s, Artificial Intelligence started a project named “denral” that was the first-ever Expert System developed. The main duty of the DENDRAL project was to observe discoveries in science and study formations of hypotheses. There are many systems developed using..Read more
ELIZA Chatbot Developed By Joseph Weizenbaum
Joseph Weizenbaum successfully developed a program, “ELIZA” that could have conversations in English with a human being. Weizenbaum’s main focus was to discover how an artificial intelligence designed mind competes with a human mind during communication termed as “superficial.” On the other side, Weizenbaum analyzed that many humans showed off..Read more
Progress in AI: Herbert Simon predictions on machines
Herbert Simon is the only scientist who said that machines would perform tasks as a man in the future. Herbert Simon had remarkable work on decision making and showed the next step in progress in AI. According to Simon, the main function of decision making is to select the best..Read more
An AI STUDENT Program Designed By Daniel Bobrow
Daniel Bobrow, a well-known Computer Scientist, created an early AI STUDENT Program developed using LISP. It allowed learners to solve word problems related to algebra. Moreover, it is considered as an early-stage milestone related to natural language processing in AI. AI Student was based on Rule-based system using the logic..Read more
SIR Computer Program By Bert Raphael’s MIT
SIR (Semantic Information Retrieval), a computer program that is designed using LISP language. It receives instructions from the human agent and answers the queries by expressing results into a restricted English language sequence. The semantics and deductive capability of the SIR computer program depend upon the program’s internal model’s construction..Read more
Stanford Cart With Radio Links By Paul W. Braisted
Braisted added an analog computer to enhance the control of the cart. This analog computer operated as a predictor to assist in steering commands. A dot is displayed on the TV screen to provide information about the predicted location towards the device that is about to move. The controllability of..Read more
Machine Perception of 3D Solids By Lawrence Gilman Roberts
Pictorial data recognition by the machine was seemed more complex than characters. Roberts wrote a program related to machine perception of 3D solids. He processed a photograph into a single line drawing; after that, the drawing is converted into a three-dimensional form, and all hidden drawing lines are removed. Using..Read more
Solutions to Analogy Problems By Thomas Evan
The analogy is designed using a complex heuristic search problem-solving program with instructions for generalization and search of transformation rules. Thomas Evan’s thesis deeply focused on finding solutions to analogy problems related to sorting given on standard IQ Exams. These solutions were the first step towards exploring analogical based reasoning..Read more
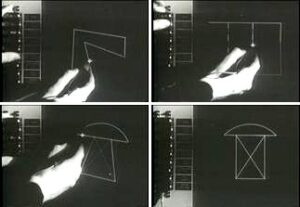
Sketchpad (Robot Draftsman) Introduced By Ivan Sutherland
Sketchpad Robot Draftsman is a computer program designed by Ivan Sutherland, the founder of Human-Computer Interaction. It has a major contribution to Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and a pioneer for computer graphics like drawings, drafting, animations, etc. Object-Oriented Programming(OOP) and Graphical User Interface (GUI.) are derivations of it in this era...Read more
Rancho Arm Developed By Victor Scheinman At SAIL
Working with SAIL, Scheiman developed the arm and hands for computers. The electric prosthetic Rancho Arm was developed by Rancho Los Amigos Hospital and has connected to the computer. To control the arm, buttons were designed, pressed by the tongue of the user. Scheinman’s major task was to maintain the..Read more
Shoebox Demonstrated By IBM
Shoebox is a computer built by I.B.M. for speech recognition and calculations of mathematical functions. The computer was able to recognize digits from 0 to 9 and 16 words spoken by humans. The box consisted of some Diode-Resistor-Logic circuitry, three analog audio filters, and a power supply. It has enhanced..Read more