The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
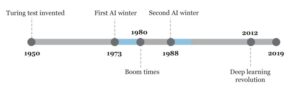
The tech we use nowadays is the outcome of a number of artificial intelligence milestones achieved by many unsung heroes. We travelled back in time and compiled a list of all significant artificial intelligence achievements that have allowed us to enjoy our current lifestyle. Let’s take a look at AI evolution over time. The timeline below highlights AI milestones that have been achieved throughout history. These achievements can be found in all areas of Artificial Intelligence. Because this is a growing timeline, new milestones will be updated on a regular basis.
Timeline
SOAR Cognitive Architecture Dissertations By John Laird & Paul Rosenbloom, And Allen Newell
The project development’s main objective was to design building blocks that are computationally fixed to build artificial agents. These agents perform various tasks such as encoding and learning different kinds of knowledge for sufficient observation of humans’ cognitive characteristics like natural language understanding, planning, problem-solving, and decision making. SOAR Cognitive..Read more
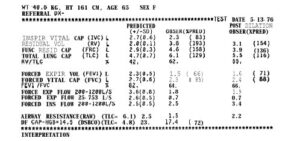
PUFF Expert System Developed By Janice S. Aikins, John C. Kunz, and Edward H. Shortliffe
An Expert System for Interpretation of Pulmonary Function Data used by at Pacific Medical Center in San Francisco. PUFF Expert System takes action by interpreting the lung function reports of the patient. It observes the lungs’ volume, patient breathing in and out conditions, and lungs’ ability for oxygen and the..Read more
RB5X Robot Developed By Joseph Bosworth
RB5X robot perceives its operating environment with RS-232 as a communication interface. Savvy or TinyBASIC can be used to program the robot. It has an arm and a transparent top of a dome shape. The robot’s input feature consists of a sonic transducer, a photodiode, and eight bumper panels. Read..Read more
Fifth Generation Computer Systems Project By The Japanese Ministry Of International Trade and Industry
The Ministry placed a budget of $850 million for the project. The Fifth Generation Computer Systems project was started to build a computer for 10-year, and the main objective was to design computers that can communicate, interpret pictures, translate languages, and think & reason like a man. These computers were..Read more
Connection Machine Designed By Danny Hillis
The connection machine provided AI new energy and is mainly used for supercomputers, also known as the Thinking Machine. It was developed to design applications related to symbolic processing and AI. Hills and colleagues wanted to arrange thousands of nodes with microprocessors to work parallel. LISP language was used to..Read more
Primal Sketch Described By David Marr and MIT Colleagues
The primal sketch has a symbolic structure. Using it with 2-D descriptions, it is possible to change an image with shades of grey. The psychophysical evidence greatly suggests these sketch implementations in human visions. However, it is not implemented automatically in human vision applications; a control structure is used to..Read more
First National Conference of the American Association of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) at Stanford University
Now the conference American Association of Artificial Intelligence is renamed “Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI).” In this conference, cognitive scientist Marvin Minsky and A.I. theorist Roger Schank predicted the second AI winter season to start soon shortly due to decreased funds and abilities to work on AI...Read more
WABOT-2 Built At Waseda University In Japan
WABOT-2 was developed under the milestone to get the first personal robot. It was declared as a “specialist robot.” A typist bot was able to do typing with his hands like a human typist. Using his mouth and ears modules, a musician robot could communicate with man, read documented music..Read more
Chinese Room Argument Program Developed by John Searle
The Chinese Room Argument Program is designed using Turing Test techniques. It describes that a program executed by a digital computer cannot hold characteristics like “mind,” “understanding,” or “consciousness.” Searle experimented by taking some Chinese characters as input, following instructions, and producing their set of Chinese characters. Searle concluded if..Read more
Blackboard Model Description By Lee Erman, Rick Hayes-Roth, Victor Lesser and Raj Reddy
In Artificial Intelligence, the blackboard model is used to build a knowledge base known as “blackboard,” where the source data stored at the knowledge base are updated iteratively when a problem occurs until the solution is obtained. Multiple processors can work together closely using separately operated threads for a system..Read more
INTERNIST Developed By Jack Myers and Harry Pople
INTERNIST is a medical expert system in which operators give input in symptoms and signs, laboratory results, and patient history. Unlike other expert systems used in medicine, it doesn’t use pattern recognition; instead, it uses algorithms to diagnose the disease using information from its internal domain. It works effectively for..Read more
BKG Program Designed By Hans Berliner
BKG program is a backgammon game developed using artificial neural networks and fuzzy logic applications to improve play features at different phases. Backgammon software facilitates the human to play the game over the Internet. First Internet Backgammon Server developed in 1992 provided the facility to play the game in real-time...Read more
Bounded Rationality Theory By Herbert A. Simon
Bounded rationality theory is finding a solution in available time using decision making that is satisfactory rather than optimal. Simon designed a new methodology for bounded rationality that provided optimal solutions in decision making, can be used in political science and economics. Simon used two concepts: “cognitive limitations” in humans,..Read more
MOLGEN Program By Mark Stefik And Peter Friedland
The MOLGEN program was written to explore applications for the domain related to molecular biology. The new version of the program had fulfilled the growing needs in the enhancement of DNA technology. The MOLGEN project and HPP work effectively in a collaborative framework for application development in different departments such..Read more
XCON Configurator Developed By John P. McDermott
XCON (eXport CONfigraturer) was designed under the domain Computer-System Components. The main responsibility of the XCON Configurator is to arrange internal components of the computer in a sensible way when a company receives an order from a customer to buy a computer. It was developed to replace “human agent” with..Read more
Boris Chess Player Developed By Applied Concepts
Chess and Intelligence always have a strong relationship. Boris is a dedicated computer used to play a chess game. David Lindsay programmed the machine to act as Boris Chess Player. It uses 256B RAM and 2.5KB ROM, 8-bit microprocessor “Fairchild F8 “. Bross was used in the “Second West Coast..Read more
Power of Meta-Level Knowledge Demonstrated By Randall Davis
How to make sure effective application of knowledge embedded in the background of a program? How to make it functional & effective so that system will continue to work with a large piece of learning? Meta-Level knowledge provides answers to these queries. Metaknowledge means ” knowledge about knowledge.” It consists..Read more
AM Program Developed By Doug Lenat
The Automated Mathematician (AM program) was developed by modifying LISP programming. Later, AM was mainly used for the interpretation of mathematical concepts related to multiplication. The numerical equivalence program can be used to find the length equality of two lists. A program designed for multiplication purposes generates a list whose..Read more
First AI Winter Event
In 1973, Sir James Lighthill’s Lighthill report was considered a trigger event for the first AI winter. The most actively funding organizations stepped back due to unsatisfactory achievements that led to customer disappointments. Due to poor Speech Understanding Research (SUR), Carnegie Mellon University lost its $3 million/year funding from DARPA..Read more
ABSTRIPS Developed By Earl Sacerdoti
ABSTRIPS (Planning In A Hierarchy of Abstraction Spaces) was considered the first program for plannings. In the program, the World as formulae set is represented by STRIPS. Each state of space set contains a World and a Goal set that is required to achieve. A stack with recursion is built..Read more
Lighthill Report By Sir James Lighthill
Sir James Lighthill divided the technology fields of A.I. into three major categories. Category A belongs to “Applications or Advance Automation,” Category C belongs to central nervous systems’ study & research. Category B belongs to applications that act as a bridge between A, and C. Category B is useful only..Read more
Computer Chess Approaches Research Paper By Claude Shannon
The first published paper on computer chess approaches was to write a program for the development of a chess game was written by Claude Shannon. According to Shannon, two approaches are required to develop computer chess: Category A programs will use pure burst force, evaluating thousands of possible moves while..Read more
Stanford Cart with A Slider By Hans Moravec
Hans Moravec worked at Stanford Cart with a slider initially developed by James L. Adams in the 1960s. Adam created a cable-handled four wheels Cart, whereas Moravec added Slider to the Cart having two wheels with steering. The Stanford Cart’s main functionality with Slider is to move a TV camera to..Read more
Freddy Robot Built By The Assembly Robotics group At Edinburgh University
Freddy robot was the first robot in the World with thinking ability like humans, visual ability in eyes, and sensation in hands. Two computer systems controlled Freddy. One was responsible for every possible move taken by the robot. The second was responsible for a set of scenarios that the robot..Read more
HAM Model Created By John Anderson and Gordon Bower
HAM (Human Associative Memory) is built in the form of a network using propositional binary trees. Every node in the tree has a unique number. At the same time, every link performs some function labeled on it. LISP is used to accomplish word indexing in the HAM model that helps..Read more
MIT Arm Developed By Victor Scheinman At MIT
MIT asked Scheinman to develop a high compact arm known as the MIT arm. DARPA provided development funds, and the vision was to design a robot as a supervisor in surgery. The direction axes intersections were created on the wrist of the arm. But now, the arm has revolute axes..Read more
Prolog Programming Language Developed By Alain Colmerauer
Prolog (Programmation en Logique) is a logical programming language strongly used in Computational Linguistics and AI. It is a nonprocedural language. It works by “What to do?” not “How to do?”, which means for any instruction execution, the man instructs the prologue-designed machine what the goal to achieve is? And..Read more
Smalltalk Language Developed By Alan Kay and Adele Goldberg
Smalltalk language is an object-oriented programming language that has a standard set of rules. It is a recursion-based language within a computer. Based on possibilities within the computer, the recursion is designed using the object of Smalltalk. A Smalltalk object can perform three tasks: (i) Hold of state (reference) (ii)..Read more
GPS Computer Program Introduced By Newell, Shaw, And Simon
GPS Computer Program logical General Problem Solver that can act like a human brain. As its name is a big hint that it can solve any type of problem. The authors developed a language IPL (Information Processing Language) to make GPS faster. Nowadays, it is possible to rewrite the GPS..Read more
MYCIN: An Expert System Developed At Stanford University
MYCIN export system written in LISP and has a simple inference engine and a knowledge base that contains ~600 rules. This system helps identify infection by providing a list of culprit bacterias and recommends antibodies and dosage of medicine adjustable with the bodyweight of the patient. Human experts used this..Read more